Information Security controls are set of rules implemented to secure various types of data and infrastructure critical to an organization. Any form or type of protection or countermeasure used to avoid, detect, counteract, or minimize security risks to physical property, information, computer systems, or any other assets is considered a security control.
Security controls in many forms can be installed to safeguard hardware, software, networks, and data from actions and events that could result in loss or harm.
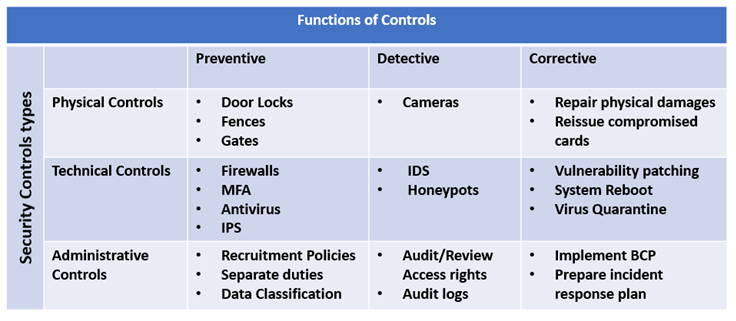
Types of Security Controls
- Physical Controls
Physical Controls are a collection of security measures that are physically applied to prevent unauthorized data access and security threats. Eg’s are gates, fences etc.
- Administrative controls
Administrative Controls are a collection of security rules, policies, procedures, or guidelines established by management to regulate access to and use of secret information. It encompasses all levels of personnel in the organization and decides who has privileged access to data resources.
Eg’s include: Data Classification, Hiring and termination policies etc.
- Technical Controls
Technical Controls are implemented to control the access of confidential information over the network using various technologies. Technical functions are involved in managing and controlling the access of the employee.
Eg’s include: Firewalls, MFA, Encryption etc.
Purpose of Security Controls
- Detective Controls
Detective controls are used to identify and inform the company about unlawful or undesired activity. It aids in the detection and response to security breaches by the use of technologies, protocols, and best practices.
- Directive Controls
Directive controls are required controls that are used to check compliance with legislation. It generally gives direction associated with the organizations have to follow, such as rules, laws, and so on.
- Preventive Controls
Preventive controls are employed in organizations to prevent or avert security issues. It aids in the reduction of unlawful actions by implementing preventative measures inside the company.
- Compensating Controls
Compensating Controls are alternate techniques that support the necessity of actually implementing security controls. The compensating Control’s job is to give a similar degree of confidence even if the real security control has been breached by the attacker.
- Deterrent Controls
Deterrent controls are used to discourage the violation of a security function, which reduces the likelihood of a purposeful attack. Deterrent controls assist in making informed judgments and deterring the employment of unsafe methods.
- Recovery Controls
After a security event, Recovery Controls are used to recover and restore the operating system to normal operation.
- Corrective Controls
Corrective controls are used to repair or lessen the impact of a security event. It covers efforts to mitigate and avoid a recurrence of the same security issue.
Sandboxing
Sandboxing is a security approach in which you utilize an isolated environment, or “sandbox,” to test your software. You execute code and evaluate code in a safe, isolated environment without harming the application, system, or platform.
Sandboxing is used to check untested or untrusted programs and is intended to prevent dangers from entering the network. Sandboxing confines the code to a test environment, preventing it from infecting or damaging the host machine or operating system.
As the name implies, this isolated test environment serves as a form of “sandbox,” in which you may experiment with various variables to observe how the software works. This is also a secure environment in which anything that goes wrong cannot actively affect your host devices.
Reverse engineering
Reverse engineering, often known as back engineering, is the practice of disassembling software, equipment, airplanes, architectural structures, and other goods in order to obtain design knowledge from them. Reverse engineering frequently entails disassembling individual components of bigger items. The reverse engineering technique determines how a part was developed so that it may be recreated. When acquiring a replacement part from an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) is not an option, businesses frequently employ this strategy.
The discipline of reverse-engineering in computer hardware and software is derived from previous industries.
Reverse engineering in software
The focus of software reverse engineering is on a program’s machine code, which is a string of 0s and 1s transmitted to the logic processor. Program language statements are used to convert machine code back to source code.
There are several situations where reverse-engineering is used to disassemble a software. One such example is to convert a program written for use with one microprocessor to another. Other examples include reconstructing lost source code, studying how a program performs certain operations, improving performance and fixing bugs or correcting errors when the source code is not available.
Reverse-engineering is also used in malware. Threat actors frequently use software code obfuscation to keep their malicious code from being discovered or understood.
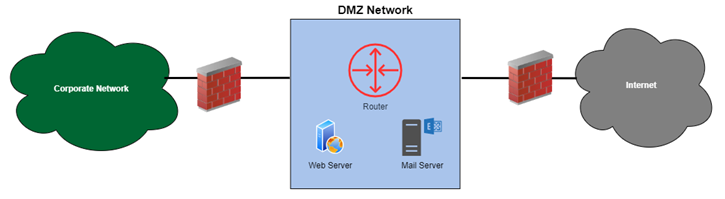
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ)
A demilitarized zone (DMZ) or perimeter network is a network region (a subnetwork) that lies between an organization’s internal network and an external network, generally the Internet, in computer security. DMZs contribute to the layered security architecture by providing subnetwork segmentation based on security requirements or policy. DMZs serve as a transit mechanism between a safe source and an insecure destination, or from an insecure source to a more secure destination. A DMZ is a screened subnet that is used for servers that are accessible from the outside in some instances.
These servers and resources are segregated and have limited LAN access to guarantee that they can be accessed through the internet but not the internal LAN. As a result, a DMZ strategy makes it more difficult for a hacker to acquire direct internet access to an organization’s data and internal systems. A corporation may reduce the risks of its Local Area Network, establishing a secure workplace while still guaranteeing employees can interact effectively and exchange information immediately over a secure connection.